STUDIES SHOW
Wild findings from a year of groundbreaking research.
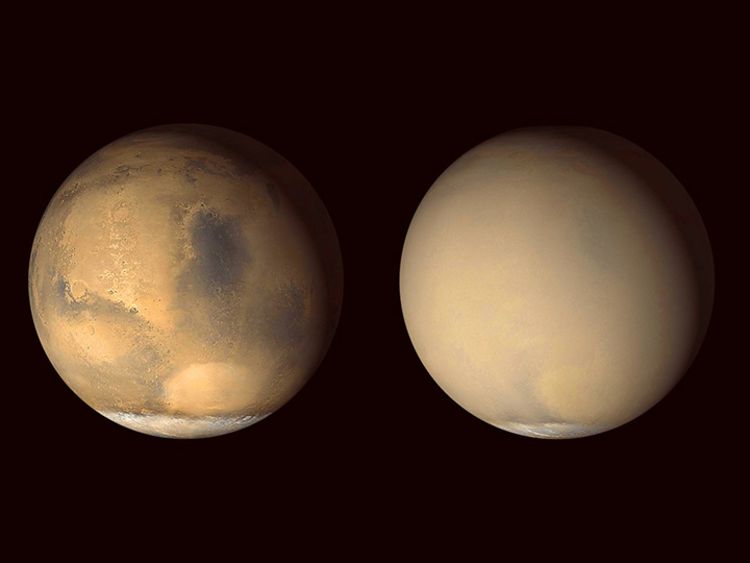
Planetary influences
Dust storms on Mars may illuminate Earth’s changing climate. Solar heat stirs up dust storms as the Red Planet’s elliptical orbit swings it closest to the sun. Surveys of the phenomenon suggest that these global dust storms play a significant role in Mars’ radiant energy budget — a finding that may be applicable to Earth’s global warming, too.

eyes on the prize
Gap junctions in our retinas could provide answers to brain disorders and degenerative diseases, according to investigations into this under-analyzed part of the human eye, its connection to our brain and how we process daily information.

bow out
When you’re wrong on Facebook, it’s better to admit it. A recent study finds that showing humility while social networking improves your reputation; users engaged in Facebook arguments who admitted they were wrong received higher reputation ratings than those who refused to cede.
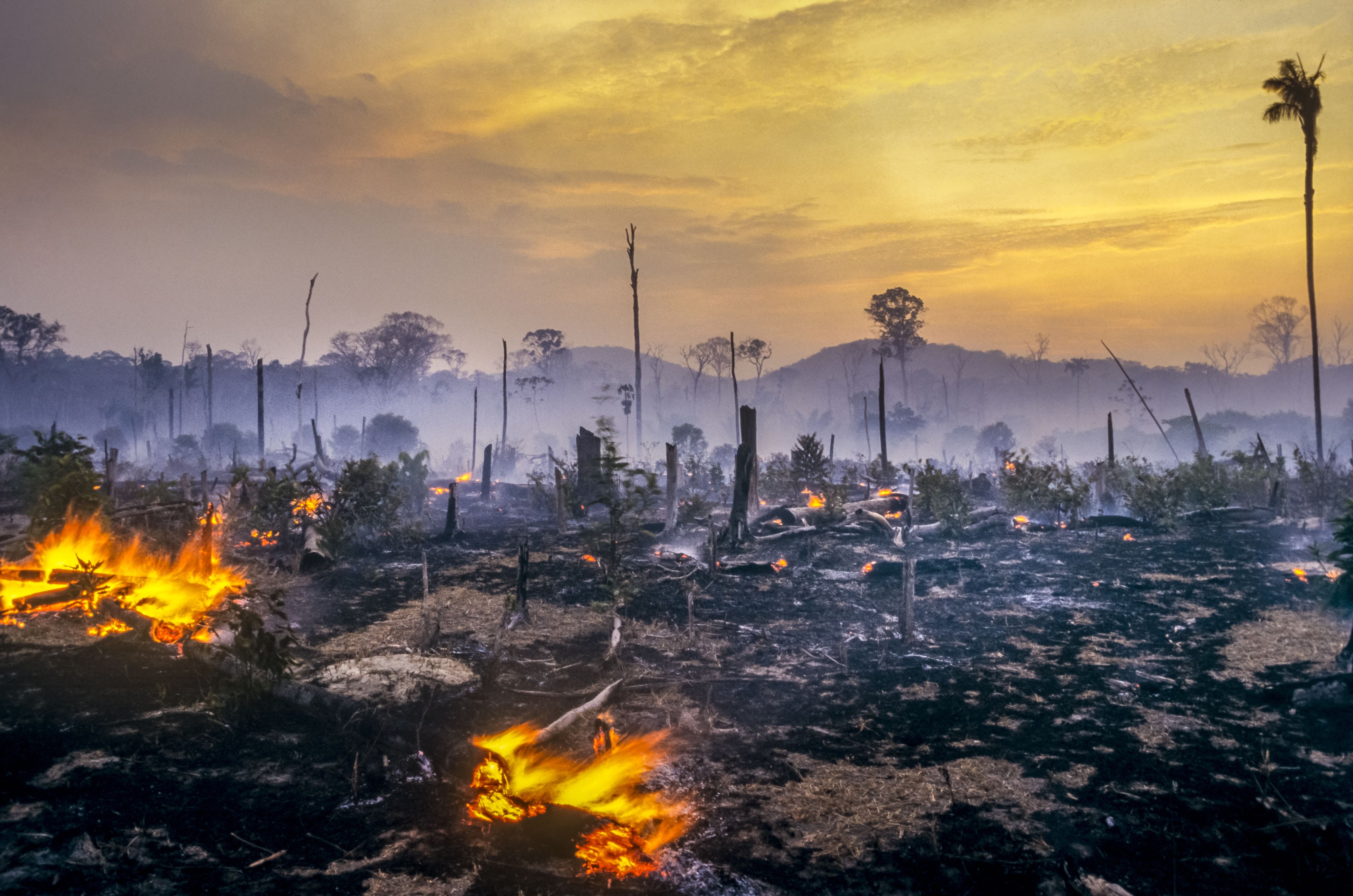

where there’s smoke
Greenhouse gas emissions from peatland fires are being underestimated by 200% to 300%. Deforestation fires in Brazil and Indonesia are affecting air pollution levels and harming animal and human health more seriously than previous data suggests.
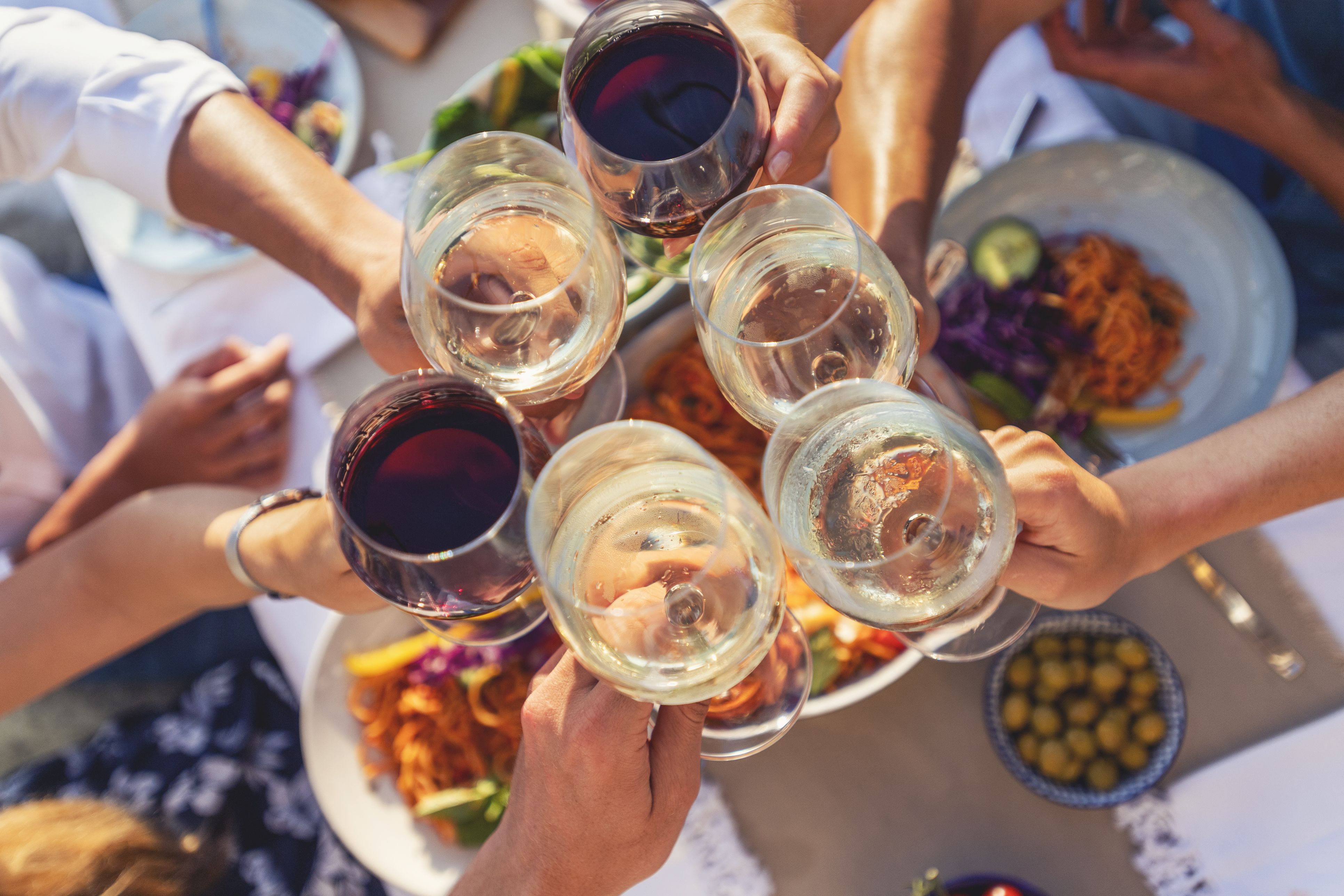

the more you know
The more you read about which wine to order, the higher your satisfaction will be. Recent research from UH’s Conrad N. Hilton College of Global Hospitality Leadership shows that restaurateurs should consider writing wine menus with “richer” descriptions than traditional menus require.

silver linings
Air pollution dropped during COVID-19 stay-at-home orders by up to 21% in 10 major cities, an air quality study found when comparing March through May 2020 to the same period in 2019. The drop was likely due to lighter vehicle traffic and slower industrial operations.

